These 3 Nutrients Improve Bone Health: As we age — or even starting in our mid- to late-thirties — bone breakdown gradually begins to outpace bone building. This shift increases the risk of developing osteoporosis and sustaining fractures, especially after menopause. However, adopting the right lifestyle habits and focusing on key nutrients can significantly help counter this risk, preserving the bone mass you’ve worked hard to build.
While getting enough protein and engaging in regular strength training are well-known strategies for supporting bone health, a recent meta-analysis sheds light on the powerful role of three essential nutrients: collagen, vitamin D, and calcium. These not only bolster bone density but also improve muscle performance and reduce fracture risk.
The study pooled data from multiple randomized clinical trials, exploring the effects of collagen peptide supplementation both independently and in combination with calcium and vitamin D. The findings revealed important new insights into how these nutrients synergize to support bone and muscle health, especially in aging populations.
Why These 3 Nutrients Matter for Bone Health
1. Collagen: The Structural Backbone of Bones
Most people are familiar with collagen for its role in maintaining youthful skin, but did you know that about 90% of the organic matrix of bone (which accounts for roughly 36% of total bone volume) consists of collagen? Collagen provides a flexible framework for minerals like calcium to attach, giving bones both structure and resilience.
Without sufficient healthy collagen, bones can become brittle, significantly increasing fracture risk. The meta-analysis showed that collagen supplementation significantly improved bone mineral density at key sites like the spine and femoral neck. Collagen also positively influenced bone turnover markers, indicating healthier bone remodeling processes.
2. Vitamin D: Enhancing Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D plays a critical role in bone health by facilitating the absorption and utilization of calcium from the diet. Without adequate vitamin D, calcium cannot effectively be absorbed, limiting its benefits for bone strength.
The study found that collagen’s positive impact on bone health was notably amplified when combined with vitamin D, resulting in more consistent improvements in bone density and muscle performance.
3. Calcium: The Bone-Building Mineral
Calcium is the mineral directly involved in forming and maintaining bone structure. It provides the hardness and strength needed to prevent fractures.
When collagen, calcium, and vitamin D were supplemented together, participants showed steady improvements in bone density and turnover markers, and moderate gains in muscle strength. This synergy proved more effective than supplementing any of the nutrients alone.
Study Findings on Bone & Muscle Health
Improved Bone Mineral Density
Collagen peptide supplementation significantly improved bone mineral density (BMD) at the spine and femoral neck. While some studies observed modest gains, others reported substantial improvements, indicating that dosage, study length, and participant characteristics can affect outcomes.
Healthier Bone Turnover
One of the most consistent results was the improvement in bone metabolism markers, suggesting that collagen supports balanced bone remodeling — an essential process where old bone is broken down and replaced by new tissue.
Enhanced Muscle Performance
Participants supplementing with collagen peptides reported moderate improvements in muscle strength and function. Better muscle performance contributes to greater stability and reduced fall risk, a critical factor in preventing fractures.

Read about: How Sleep Disorders and Unhealthy Lifestyles Impact Mental Health – And Tips to Avoid Them
Practical Tips to Boost Your Bone and Muscle Health
Collagen Supplements
Collagen peptides aren’t found in meaningful amounts in a typical diet, so supplementation is especially helpful. Look for collagen powders that provide at least 15 grams of collagen peptides per serving for optimal bone and muscle support.
Vitamin D Sources
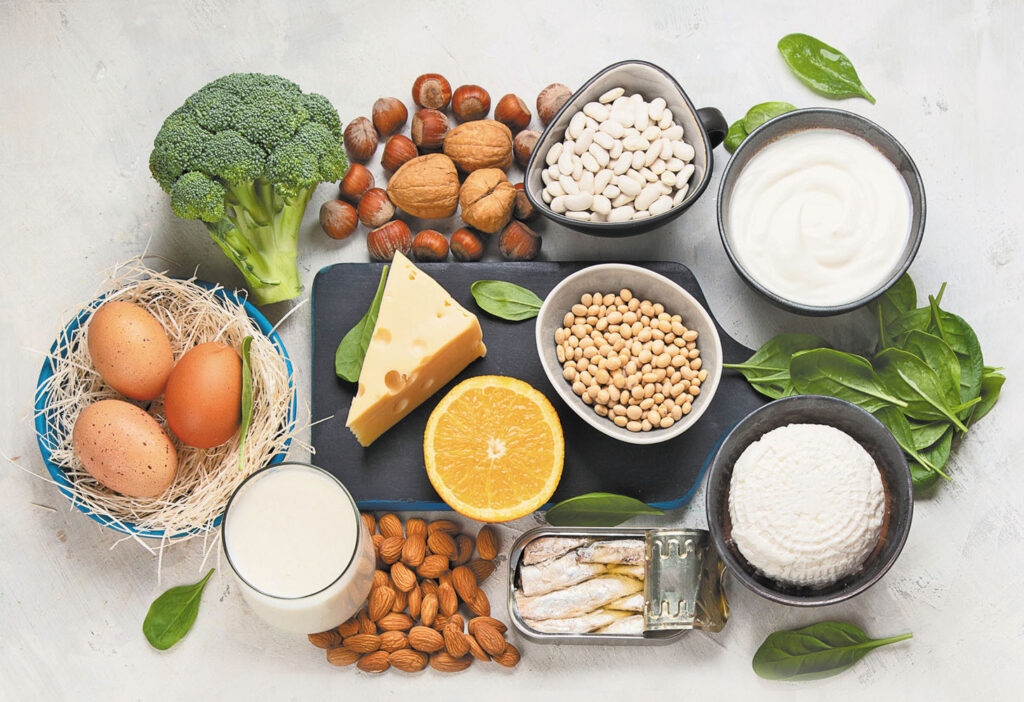
Fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods provide some vitamin D, but most people benefit from supplements, especially in regions with limited sun exposure. High-potency vitamin D supplements ensure adequate intake and absorption.
Calcium-Rich Foods and Supplements
Calcium can be found in dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, leafy greens like spinach and kale, and canned fish with bones, such as sardines. For individuals not meeting dietary calcium needs, supplements are a safe and effective option.
Conclusion
The Mayo Clinic study underscores the importance of not just focusing on traditional bone health strategies like protein intake and exercise but also incorporating key nutrients such as collagen, vitamin D, and calcium. Together, they form a potent trio that enhances bone mineral density, supports muscle strength, and lowers fracture risk.
With aging, especially post-menopause, the risk of osteoporosis and fractures becomes a real concern. Incorporating these nutrients into your daily routine can make a meaningful difference in preserving bone health and overall mobility.
Consult your healthcare provider to tailor a supplementation plan based on your individual needs and health status. Regular bone density screenings and strength training exercises, coupled with a balanced intake of these nutrients, empower you to maintain a strong, healthy body as you age.
Also read: HGML Recruitment 2025 – जनरल मैनेजर (इंजीनियरिंग) पद के लिए आवेदन करें
FAQs These 3 Nutrients Improve Bone Health
1. Why is collagen important for bone health?
Collagen constitutes about 90% of the bone’s organic matrix and provides the structural framework that supports mineral attachment. It helps maintain bone flexibility and resilience, preventing brittleness that can lead to fractures, especially as we age.
2. How does vitamin D contribute to bone strength?
Vitamin D enhances the body’s ability to absorb calcium from food or supplements, allowing calcium to be effectively used in bone formation and maintenance. Without enough vitamin D, calcium absorption is compromised, weakening bones over time.
3. Can I get enough calcium from my diet alone?
While calcium is found in dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, many people do not meet their recommended daily intake through diet alone. Supplements provide a reliable solution to ensure adequate calcium levels, especially in older adults or those with dietary restrictions.
4. What is the best way to take collagen supplements for bone health?
For effective bone and muscle support, it’s recommended to consume at least 15 grams of collagen peptides per serving. Collagen powders are a convenient option. Combining them with vitamin D and calcium supplements provides the best synergistic effect.
5. Are there any side effects of collagen supplementation?
Collagen supplements are generally considered safe when taken as directed. Mild digestive discomfort can occur initially. It’s important to choose high-quality products free of unnecessary additives and consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.